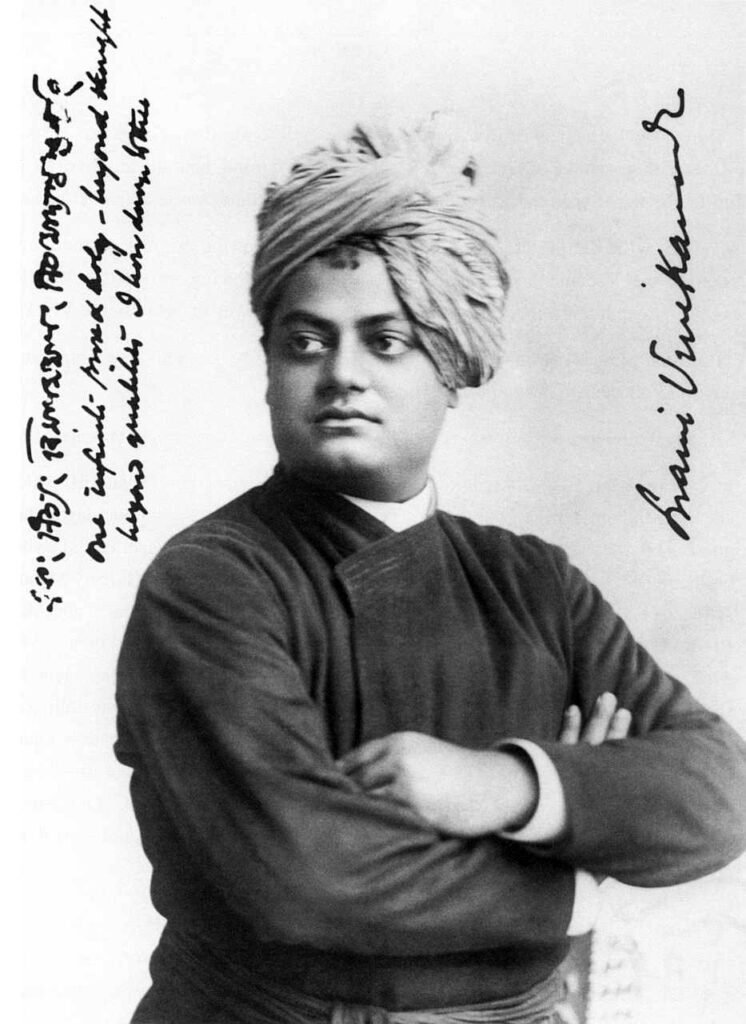
स्वामी विवेकानंद भारतीय समाज के एक महान विचारक, योगी, संत, और राष्ट्रवादी थे, जिनका जीवन दर्शन, शिक्षा, और सेवा के प्रति समर्पण आज भी प्रेरणा का स्रोत है। उनका जन्म 12 जनवरी 1863 को हुआ था, और उनकी जयंती को ‘राष्ट्रीय युवा दिवस’ के रूप में मनाया जाता है। स्वामी विवेकानंद ने भारतीय संस्कृति, वेदांत, और योग के महत्व को पश्चिमी दुनिया में प्रस्तुत किया और भारतीय समाज को आत्मनिर्भर और जागरूक बनाने के लिए प्रेरित किया।
प्रारंभिक जीवन और शिक्षा
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जन्म नरेन्द्रनाथ दत्त के रूप में हुआ था। उनके पिता, श्री विश्वनाथ दत्त, कलकत्ता उच्च न्यायालय में वकील थे, और माता, भुवनेश्वरी देवी, एक धार्मिक विचारों वाली महिला थीं। नरेन्द्रनाथ की प्रारंभिक शिक्षा घर पर ही हुई, और बाद में उन्होंने प्रेसीडेंसी कॉलेज से स्नातक की डिग्री प्राप्त की। वे दर्शन, इतिहास, और संस्कृत में निपुण थे और बचपन से ही धार्मिक और आध्यात्मिक रुचि रखते थे।
रामकृष्ण परमहंस से मिलन
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन एक महत्वपूर्ण मोड़ उस समय आया जब वे श्री रामकृष्ण परमहंस से मिले। रामकृष्ण परमहंस के सान्निध्य में आकर नरेन्द्रनाथ ने आत्मज्ञान की प्राप्ति की और ‘स्वामी विवेकानंद’ के नाम से प्रसिद्ध हुए। रामकृष्ण परमहंस के प्रति उनकी श्रद्धा और समर्पण ने उन्हें जीवन में एक नई दिशा दी।
भारत भ्रमण और सामाजिक जागरूकता
स्वामी विवेकानंद ने 25 वर्ष की आयु में संन्यास लिया और पूरे भारतवर्ष की यात्रा की। इस यात्रा के दौरान उन्होंने भारतीय समाज की गरीबी, अंधविश्वास, और सामाजिक असमानता को देखा और समाज सुधार के लिए कार्य करने का संकल्प लिया।
शिकागो धर्म महासभा (1893)
स्वामी विवेकानंद की अंतरराष्ट्रीय पहचान 1893 में शिकागो धर्म महासभा में उनके ऐतिहासिक भाषण से हुई। इस भाषण में उन्होंने ‘आपका भारत’ शब्दों से धर्म, सहिष्णुता, और मानवता का संदेश दिया। उन्होंने भारतीय संस्कृति और वेदांत के महत्व को पश्चिमी दुनिया में प्रस्तुत किया और भारतीय समाज को गर्व महसूस कराया।
रामकृष्ण मिशन की स्थापना
स्वामी विवेकानंद ने 1 मई 1897 को रामकृष्ण मिशन की स्थापना की। इस मिशन का उद्देश्य वेदांत दर्शन का प्रचार करना, मानव सेवा करना, और समाज में सुधार लाना था। मिशन ने शिक्षा, स्वास्थ्य, और सामाजिक सेवा के क्षेत्र में महत्वपूर्ण कार्य किए।
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन शिक्षा पर दृष्टिकोण
स्वामी विवेकानंद का मानना था कि शिक्षा का उद्देश्य केवल ज्ञान प्राप्ति नहीं, बल्कि चरित्र निर्माण और आत्मनिर्भरता है। उन्होंने भारतीय शिक्षा प्रणाली में सुधार की आवश्यकता पर बल दिया और युवाओं को आत्मविश्वास और स्वावलंबन के लिए प्रेरित किया।
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन जीवन दर्शन और योगदान
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन दर्शन आत्मनिर्भरता, सेवा, और समाज सुधार पर आधारित था। उन्होंने भारतीय समाज को जागरूक किया और युवाओं को अपने कर्तव्यों के प्रति समर्पित रहने की प्रेरणा दी। उनकी शिक्षाएं आज भी समाज में सकारात्मक परिवर्तन लाने के लिए मार्गदर्शक हैं।
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन निष्कर्ष
स्वामी विवेकानंद का जीवन एक प्रेरणा है जो हमें अपने कर्तव्यों के प्रति जागरूक और समर्पित रहने की प्रेरणा देता है। उनकी शिक्षाएं और कार्य आज भी समाज में सकारात्मक परिवर्तन लाने के लिए मार्गदर्शक हैं। उनका जीवन यह सिद्ध करता है कि एक व्यक्ति अपने दृढ़ संकल्प और समर्पण से समाज में महान परिवर्तन ला सकता है।
स्वामी विवेकानंद की शिक्षाओं को आत्मसात कर हम एक जागरूक और समर्पित समाज की स्थापना कर सकते हैं। उनका जीवन यह संदेश देता है कि यदि हम अपने कर्तव्यों के प्रति जागरूक और समर्पित रहें, तो हम समाज में सकारात्मक परिवर्तन ला सकते हैं।

Swami Vivekananda: A Comprehensive Overview
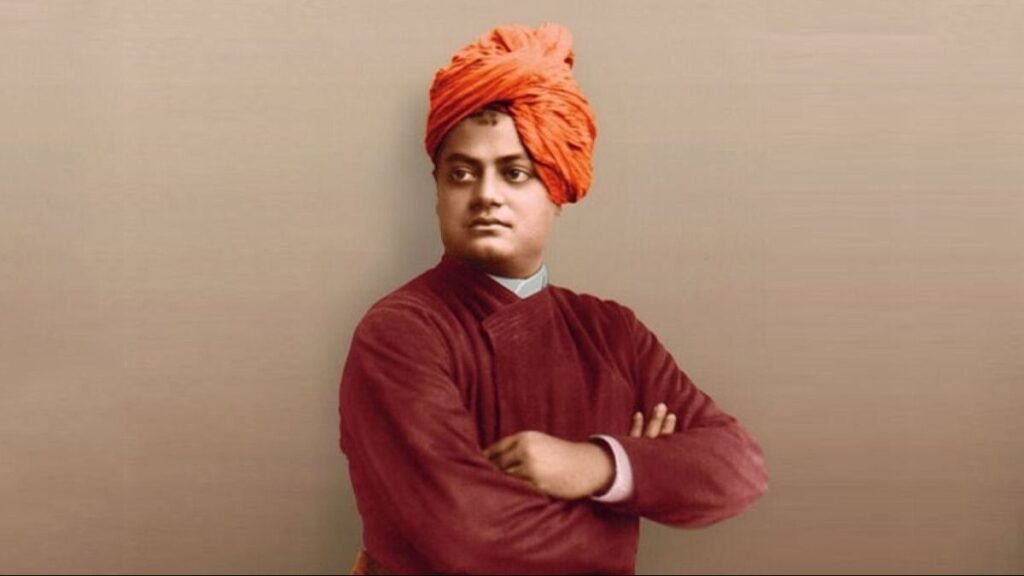

Introduction
Swami Vivekananda (1863–1902) was one of India’s greatest spiritual leaders, philosophers, and reformers. He played a pivotal role in introducing Indian philosophy, especially Vedanta and Yoga, to the Western world. Beyond spiritual teachings, Vivekananda was a social reformer, advocating education, equality, and service to humanity. His message of self-confidence, self-realization, and universal brotherhood continues to inspire people worldwide.
Early Life and Family
Swami Vivekananda was born as Narendranath Datta on January 12, 1863, in Kolkata (then Calcutta), India. His father, Vishwanath Datta, was a lawyer, and his mother, Bhuvaneshwari Devi, was a deeply religious woman. From an early age, Narendra exhibited a keen intellect and spiritual curiosity. He was drawn to philosophy, religion, and the mysteries of existence.
- Education: Narendra received his primary education at home and later attended the Presidency College, Kolkata. He studied philosophy, history, and Western logic while also learning Sanskrit and exploring Indian scriptures like the Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, and epics like Mahabharata and Ramayana.
- Early Influences: Young Narendra was influenced by thinkers, saints, and social reformers. His mother instilled in him values of compassion and service, while his father nurtured critical thinking.
Meeting Ramakrishna Paramahamsa
A turning point in Narendra’s life was his encounter with Ramakrishna Paramahamsa, a mystic and spiritual master. Under Ramakrishna’s guidance:
- He realized the importance of spiritual practice and direct experience of God.
- He embraced the ideal of renunciation and eventually became a monk.
- He was given the monastic name Swami Vivekananda, which means “the bliss of discernment or wisdom.”
Ramakrishna’s teachings shaped Vivekananda’s worldview, emphasizing that all religions lead to the same ultimate truth, and that serving humanity is the highest form of worship.
Travels Across India
After taking formal monastic vows, Vivekananda traveled extensively across India to:
- Understand the plight of the common people.
- Experience social, economic, and spiritual realities firsthand.
- Spread the message of unity, self-reliance, and empowerment.
During his travels, he witnessed poverty, caste discrimination, and social injustice, which strengthened his resolve to work for societal reform.
The Chicago Parliament of Religions, 1893
Swami Vivekananda gained worldwide recognition when he represented Hinduism at the World’s Parliament of Religions in Chicago, 1893.
- Famous Speech: He began his address with “Sisters and Brothers of America,” which received a standing ovation.
- Message: He spoke about religious tolerance, universal brotherhood, and the spiritual heritage of India.
- This event introduced Western audiences to Vedanta philosophy and Indian spirituality.
Vivekananda’s presence in the West also helped establish India as a land of profound spiritual knowledge.
Establishment of Ramakrishna Mission
Upon returning to India, Vivekananda founded the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897 to:
- Promote spiritual growth through education and service.
- Provide healthcare, disaster relief, and social upliftment.
- Integrate spiritual teachings with practical social action.
The mission remains active worldwide, continuing Vivekananda’s vision of service to humanity as service to God.
Philosophy and Teachings
Swami Vivekananda’s teachings focused on several core principles:
- Universalism: All religions are valid paths to the same truth.
- Self-Realization: Each individual has immense potential that can be realized through discipline and spiritual practice.
- Service to Humanity: Helping the poor, the sick, and the needy is the highest spiritual duty.
- Education: Education should develop character, self-confidence, and practical skills, not just knowledge.
- Empowerment of Youth: He believed that the youth are the leaders of society and should be inspired to work for nation-building.
Views on Education
Vivekananda emphasized holistic education:
- Education should awaken moral consciousness and develop mental strength.
- Learning must cultivate self-reliance, courage, and ethical values.
- He urged India to modernize its education system while retaining spiritual and cultural roots.
Social Reform and Nation-Building
Swami Vivekananda’s vision extended beyond spiritual teachings:
- He encouraged social reform by opposing caste discrimination and promoting equality.
- He inspired Indians to embrace national pride while retaining spiritual humility.
- His message empowered marginalized communities, emphasizing dignity and potential.
Legacy and Influence
Swami Vivekananda passed away on July 4, 1902, at the age of 39. Despite his short life, his impact has been immense:
- Inspired leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, Subhas Chandra Bose, and many others.
- Spread Indian philosophy across the world.
- Motivated youth to pursue education, self-confidence, and national service.
His birthday, January 12, is celebrated as National Youth Day in India.
Conclusion
Swami Vivekananda’s life teaches us the importance of discipline, courage, and selfless service. He exemplified how spirituality and social responsibility can coexist. His vision of universal brotherhood, education, and empowerment continues to guide individuals and nations.
Vivekananda’s message is timeless: “Arise, awake, and stop not until the goal is reached




