Reproduction in Animals Notes
→ Reproduction is essential for the continuation of the species.
→ Types of Reproduction:
Sexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
→ In sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse.
→ The gamete (fertile stem) is the first cell of a new offspring.
→ Sexual reproduction occurs in humans.
→ The male reproductive organs in humans are the testes, vas deferens, and penis.
→ In men, the testes produce sperm cells.
→ The structure of a sperm cell consists of three parts: the head, middle part, and tail.
→ The female reproductive organs in humans are the ovaries, oviducts, and uterus.
→ In women, the ovaries secrete one sperm each month.
→ In humans, sperm and testes are microscopic in size.
→ In the process of fertilization, sperm and testes combine to form a zygote (fertilized egg).
→ Types of fertilization:
Internal fertilization and
External fertilization
In internal fertilization, the zygote forms inside the female body.
→ In external fertilization, the zygote forms outside the female body in water.
→ In asexual animals, the embryo develops inside the female body and the young are born.
→ In oviparous animals, the embryo develops inside the egg and the young hatch when the egg shell breaks.
→ In some animals, the newborn cubs differ from the adult. Such newborn cubs undergo certain changes and develop into adults.
→ IVF (in vitro fertilization) is a boon for couples suffering from infertility.
→ In IVF, the embryo is fertilized outside the body and the zygote is implanted in the uterus.
→ Asexual reproduction involves only one organism.
→ Asexual reproduction occurs by fission in amoeba and budding in hydra.
→ Dolly the sheep is the result of successful mammalian cloning. Glossary
→ Asexual reproduction: The production of offspring by a single parent without the production of reproductive cells.
→ Binary fission: Asexual reproduction occurs when a unicellular organism divides to produce two offspring that behave as independent organisms.
→ Budding: Asexual reproduction in which a young organism arises from a structure that develops on the surface of the body.
→ Egg: A developed embryo with a strong shell that is shed by the animal.
→ Embryo: A multicellular organism formed by the continuous division of gametes.
→ Fertilization: The process of gamete formation by the union of sperm and egg.
→ External fertilization: The formation of gametes outside the body of a female animal.
→ Internal fertilization: The formation of gametes inside the body of a female animal.
→ Poetus: A fully developed embryo with all its body parts identified.
→ Zygote: A single-celled structure containing a gamete nucleus formed by the fusion of a sperm and an egg.
→ Sperm: Male reproductive organ: Male reproductive cells produced from sperm.
→ Sexual reproduction: A reproductive system in which two parents participate to produce offspring.
→ Metamorphosis: A series of changes that occur in a young organism that is different in size from the parent, and as it grows and develops, it takes on the shape of the parent.
→ Oviparous animals: Animals that lay eggs, in which the embryo develops in the egg outside the body and a young animal is formed.
→ Viviparous animals: Animals in which the embryo develops inside the mother’s body, and the developing embryo is nourished by the mother’s body and she gives birth to the young.
Reproduction in Animals Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
Answer:
Reproduction is a very important process for the living organisms. Reproduction is essential for the continuation of a species.
Question 2.
Describe the process of fertilisation in human beings.
Answer:
In human, sexual reproduction takes place. In human beings internal fertilisation takes place. Male releases sperms inside female’s body. Sperms and ovum fuse together in fallopian tube to form zygote. During this process the nucleus of sperm fuses with the nucleus of ovum to form a single nucleus. This complete process is called fertilisation.
Question 3.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
(a) Internal fertilisation occurs
(i) in female body
(ii) outside female body
(iii) in male body
(iv) outside male body.
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
(i) fertilisation
(ii) metamorphosis
(iii) embedding
(iv) budding.
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
(i) none
(ii) one
(iii) two
(iv) four
Answer:
(a) (i) in female body
(b) (ii) metamorphosis
(c) (ii) one.
Question 4.
Indicate whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
(b) Each sperm is a single cell.
(c) External fertilisation takes place in frog.
(d) A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete.
(e) Egg laid after fertilisation is made up of a single cell.
(f) Amoeba reproduces by budding.
(g) Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction.
(h) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction.
(i) A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation.
(j) An embryo is made up of a single cell.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
(e) True
(f) False
(g) False
(h) True
(i) True
(j) False
Question 5.
Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
Answer:
Zygote:
- It contains only single cell.
- It is formed by the fusion of ovum and sperm.
Foetus:
- It contains many cells.
- It is formed by repeated divisions of zygote. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction
Question 6.
Define asexual reproduction. in animals.
Answer:
The type of reproduction in which only single parent is involved is called asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction takes place by different methods:
(i) Budding: This process takes place in hydra and yeast. A part of organism starts bulging out. Slowly it grows and develops into a separate individual.
(ii) Binary Fission: This type of re-production takes place in amoeba. The nucleus of amoeba gets divided into two followed by division of their bodies, each part getting one nucleus. Each part developed into separate amoeba. This type of reproduction is common in unicellular organisms.
Question 7.
In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Answer:
In uterus.
Question 8.
What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
Answer:
The transformation of larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis. Example: In frog and butterfly.
Question 9.
Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
Answer:
The internal fertilisation takes place inside the body of female but the external fertilisation takes place outside the body of female.
In internal fertilisation, the sperms are released in female’s body by the male while in external fertilisation sperms are released in open like in water.
Question 10.
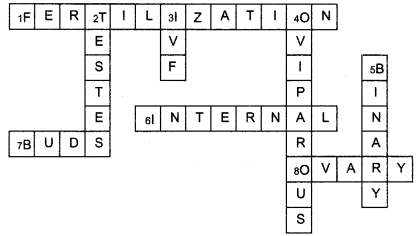
Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below:
Across:
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilisation in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
Down:
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for in vitro fertilization.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.
Answer:
जंतुओं में प्रजनन Notes
→ प्रजातियों की निरंतरता के लिए प्रजनन आवश्यक है।
→ प्रजनन के प्रकार:
लैंगिक प्रजनन
अलैंगिक प्रजनन
→ लैंगिक प्रजनन में, नर और मादा युग्मक संलयित होते हैं।
→ युग्मक (उपजाऊ तना) नई संतान की पहली कोशिका होती है।
→ मनुष्यों में लैंगिक प्रजनन होता है।
→ मनुष्यों में नर प्रजनन अंग वृषण, शुक्रवाहिनी और लिंग हैं।
→ पुरुषों में, वृषण शुक्राणु कोशिकाओं का उत्पादन करते हैं।
→ शुक्राणु कोशिका की संरचना में तीन भाग होते हैं: सिर, मध्य भाग और पूंछ।
→ मनुष्यों में मादा प्रजनन अंग अंडाशय, अंडवाहिनी और गर्भाशय हैं।
→ महिलाओं में, अंडाशय हर महीने एक वृषण स्रावित करते हैं।
→ मनुष्यों में, शुक्राणु और वृषण आकार में सूक्ष्म होते हैं।
→ निषेचन की प्रक्रिया में, शुक्राणु और वृषण मिलकर युग्मनज (उर्वरक) बनाते हैं।
→ निषेचन के प्रकार:
आंतरिक निषेचन और
बाह्य निषेचन
आंतरिक निषेचन में, युग्मनज मादा शरीर के अंदर बनता है।
→ बाह्य निषेचन में, युग्मनज मादा शरीर के बाहर पानी में बनता है।
→ अलैंगिक प्राणियों में, भ्रूण मादा शरीर के अंदर विकसित होता है और बच्चे पैदा होते हैं।
→ अंडप्रजक प्राणियों में, भ्रूण अंडे के अंदर विकसित होता है और अंडे का खोल टूटने पर बच्चे निकलते हैं।
→ कुछ प्राणियों में, नवजात शावक वयस्क प्राणी से भिन्न होते हैं। ऐसे नवजात शावक कुछ परिवर्तनों से गुजरते हैं और वयस्क प्राणी में परिवर्तित हो जाते हैं।
→ आईवीएफ (इन विट्रो फर्टिलाइजेशन) बांझपन से पीड़ित दम्पतियों के लिए एक वरदान है।
→ आईवीएफ में, भ्रूण को शरीर के बाहर निषेचित किया जाता है और युग्मनज को गर्भाशय में प्रत्यारोपित किया जाता है।
→ अलैंगिक प्रजनन में केवल एक जीव शामिल होता है।
→ अलैंगिक प्रजनन अमीबा में विखंडन और हाइड्रा में मुकुलन द्वारा होता है।
→ डॉली भेड़ सफल स्तनधारी क्लोनिंग का परिणाम है। शब्दावली
→ अलैंगिक प्रजनन: प्रजनन कोशिकाओं के उत्पादन के बिना एकल जनक द्वारा संतानों का उत्पादन।
→ द्विविखंडन: अलैंगिक प्रजनन तब होता है जब एक एककोशिकीय जीव विभाजित होकर दो संतानें उत्पन्न करता है जो स्वतंत्र जीवों की तरह व्यवहार करती हैं।
→ मुकुलन: अलैंगिक प्रजनन जिसमें शरीर की सतह पर विकसित होने वाली एक संरचना से एक शिशु जीव उत्पन्न होता है।
→ अंडे: एक विकसित भ्रूण जिसका एक मजबूत खोल होता है और जिसे जानवर द्वारा गिराया जाता है।
→ भ्रूण: युग्मकों के निरंतर विभाजन से निर्मित एक बहुकोशिकीय जीव।
→ निषेचन: शुक्राणु और अंडाणु के मिलन से युग्मक निर्माण की प्रक्रिया।
→ बाह्य निषेचन: मादा पशु के शरीर के बाहर युग्मक का निर्माण।
→ आंतरिक निषेचन: मादा पशु के शरीर के अंदर युग्मक का निर्माण।
→ पोएटस: एक पूर्ण विकसित भ्रूण जिसके शरीर के सभी अंग पहचाने जा चुके हों।
जीएसईबी कक्षा 8 विज्ञान नोट्स अध्याय 9 जंतुओं में प्रजनन
→ युग्मनज: एक एकल-कोशिका संरचना जिसमें एक युग्मक केंद्रक होता है जो शुक्राणु और अंडाणु के संलयन से बनता है।
→ शुक्राणु: नर प्रजनन अंग: शुक्राणु से उत्पन्न नर प्रजनन कोशिकाएँ।
→ लैंगिक प्रजनन: एक प्रजनन प्रणाली जिसमें दो जनक संतान उत्पन्न करने के लिए भाग लेते हैं।
→ कायांतरण: माता-पिता से भिन्न आकार वाले शिशु जीव में होने वाले परिवर्तनों की एक श्रृंखला, वृद्धि और विकास के साथ माता-पिता का रूप धारण कर लेती है।
→ अण्डज (ओविपेरस) जन्तु: वे जन्तु जो अंडे देते हैं, जिनमें भ्रूण शरीर के बाहर अंडे में विकसित होता है और एक नवजात जन्तु का निर्माण होता है।
→ सजीव (वाइविपेरस) जन्तु: वे जन्तु जिनमें भ्रूण माँ के शरीर के अंदर विकसित होता है और विकासशील भ्रूण का पोषण माँ के शरीर द्वारा प्रदान किया जाता है और वह बच्चे को जन्म देती है।
पशुओं में प्रजनन पाठ्यपुस्तक प्रश्न और उत्तर
प्रश्न 1.
जीवों में प्रजनन के महत्व की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर:
जीवों के लिए प्रजनन एक अत्यंत महत्वपूर्ण प्रक्रिया है। किसी प्रजाति की निरंतरता के लिए प्रजनन आवश्यक है।
प्रश्न 2.
मनुष्यों में निषेचन की प्रक्रिया का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर:
मनुष्य में लैंगिक प्रजनन होता है। मनुष्यों में आंतरिक निषेचन होता है। नर मादा के शरीर के अंदर शुक्राणु छोड़ता है। शुक्राणु और अंडाणु फैलोपियन ट्यूब में मिलकर युग्मनज बनाते हैं। इस प्रक्रिया के दौरान शुक्राणु का केंद्रक अंडाणु के केंद्रक के साथ मिलकर एक केंद्रक बनाता है। इस संपूर्ण प्रक्रिया को निषेचन कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
सबसे उपयुक्त उत्तर चुनें:
(a) आंतरिक निषेचन होता है
(i) मादा शरीर में
(ii) मादा शरीर के बाहर
(iii) नर शरीर में
(iv) नर शरीर के बाहर।
(b) एक टैडपोल किस प्रक्रिया द्वारा एक वयस्क मेंढक में विकसित होता है?
(i) निषेचन
(ii) कायापलट
(iii) अंतःस्थापन
(iv) मुकुलन।
(c) युग्मनज में उपस्थित केन्द्रकों की संख्या है:
(i) कोई नहीं
(ii) एक
(iii) दो
(iv) चार
उत्तर:
(a) (i) मादा शरीर में
(b) (ii) कायापलट
(c) (ii) एक।
प्रश्न 4.
बताएँ कि निम्नलिखित कथन सत्य हैं या असत्य।
(a) अंडप्रजक जंतु बच्चों को जन्म देते हैं।
(b) प्रत्येक शुक्राणु एक एकल कोशिका होता है।
(c) मेंढक में बाह्य निषेचन होता है।
(d) युग्मक नामक कोशिका से एक नया मानव विकसित होता है।
(e) निषेचन के बाद दिया गया अंडा एकल कोशिका से बना होता है।
(f) अमीबा मुकुलन द्वारा प्रजनन करता है।
(g) अलैंगिक प्रजनन में भी निषेचन आवश्यक है।
(h) द्विविभाजन अलैंगिक प्रजनन की एक विधि है।
(i) निषेचन के परिणामस्वरूप युग्मनज बनता है।
(j) भ्रूण एक कोशिका से बना होता है।
उत्तर:
(a) असत्य
(b) सत्य
(c) सत्य
(d) असत्य
(e) सत्य
(f) असत्य
(g) असत्य
(h) सत्य
(i) सत्य
(j) असत्य
प्रश्न 5.
युग्मनज और भ्रूण के बीच दो अंतर बताइए।
उत्तर:
युग्मनज:
इसमें केवल एक कोशिका होती है।
यह अंडाणु और शुक्राणु के संलयन से बनता है।
भ्रूण:
इसमें कई कोशिकाएँ होती हैं।
यह युग्मनज के बार-बार विभाजन से बनता है। अलैंगिक प्रजनन की दो विधियों का वर्णन कीजिए।
प्रश्न 6.
अलैंगिक प्रजनन को परिभाषित कीजिए। जंतुओं में।
उत्तर:
वह प्रजनन जिसमें केवल एक ही जनक शामिल होता है, अलैंगिक प्रजनन कहलाता है। अलैंगिक प्रजनन विभिन्न विधियों द्वारा होता है:
(i) मुकुलन: यह प्रक्रिया हाइड्रा और यीस्ट में होती है। जीव का एक भाग बाहर की ओर उभरने लगता है। धीरे-धीरे यह बढ़ता है और एक अलग जीव के रूप में विकसित होता है।
(ii) द्विविभाजन: इस प्रकार का पुनरुत्पादन अमीबा में होता है। अमीबा का केंद्रक दो भागों में विभाजित हो जाता है, जिसके बाद उनके शरीर का विभाजन होता है, प्रत्येक भाग को एक केंद्रक प्राप्त होता है। प्रत्येक भाग अलग अमीबा में विकसित होता है। इस प्रकार का प्रजनन एककोशिकीय जीवों में सामान्य है।
प्रश्न 7.
भ्रूण किस मादा प्रजनन अंग में स्थापित होता है?
उत्तर:
गर्भाशय में।
प्रश्न 8.
कायापलट क्या है? उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर:
लार्वा का अत्यधिक परिवर्तनों के माध्यम से वयस्क में परिवर्तन कायापलट कहलाता है। उदाहरण: मेंढक और तितली में।
प्रश्न 9.
आंतरिक निषेचन और बाह्य निषेचन में अंतर स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
आंतरिक निषेचन मादा के शरीर के अंदर होता है, लेकिन बाह्य निषेचन मादा के शरीर के बाहर होता है।
आंतरिक निषेचन में, नर द्वारा शुक्राणु मादा के शरीर में छोड़े जाते हैं, जबकि बाह्य निषेचन में शुक्राणु खुले में, जैसे पानी में, छोड़े जाते हैं।
